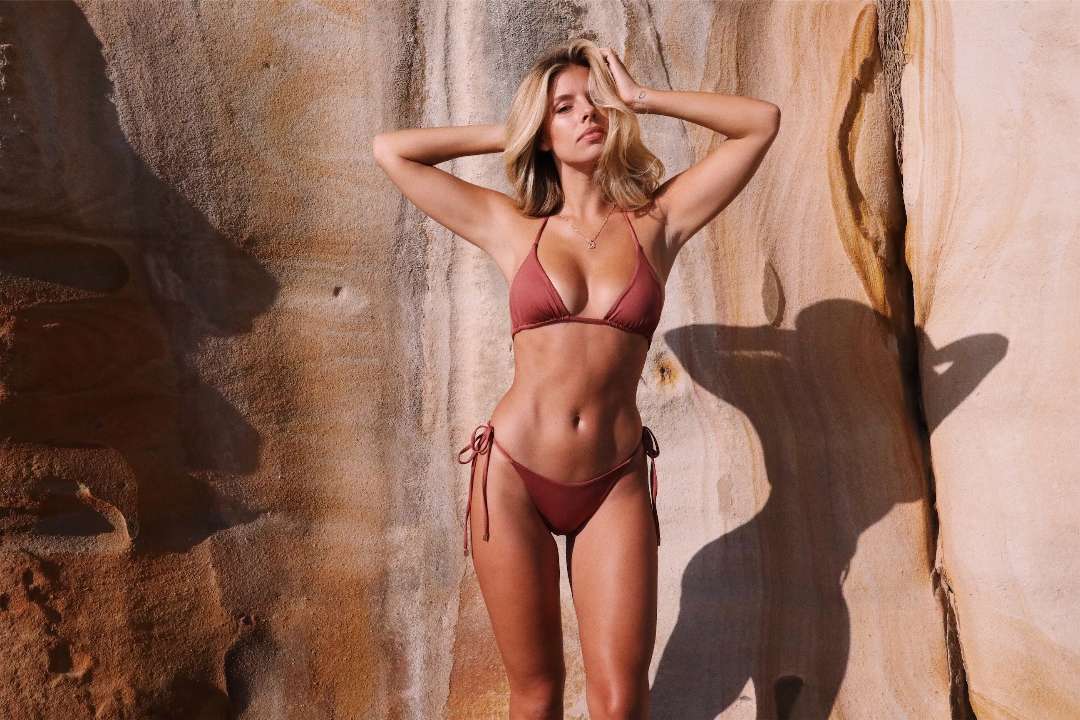

There’s no such thing as a permanent tan. You can do certain things to make your tan last longer, but it won’t last forever. Here’s everything you need to know about getting a tan – and maintaining it.
A tan has no medicinal benefits, yet many of us love the appearance of tanned skin. When sunlight or artificial ultraviolet (UV) rays strike the skin, a pigment called melanin forms. Melanin is responsible for the brown glow associated with tans, but it is also the skin’s way of defending itself from harm from the sun.
Tans from outdoor exposure are caused mainly by UVA radiation from the sun, while the earth’s ozone layer absorbs most of the sun’s UVB rays. Tanning beds typically emit a combination of UVA and UVB rays. UVB rays have greater intensity than UVA rays, may directly damage your DNA, and are responsible for most skin malignancies.
Spray tans, in which the colour additive dihydroxyacetone (DHA) is sprayed uniformly to darken skin cells temporarily, are a popular way to achieve a tan without exposure to damaging UV radiation.
Tans will remain for varying amounts of time depending on how you got it in the first place (UV rays or spray). Tans usually lasts 7 to 10 days until your skin spontaneously exfoliates and regenerates. You can do certain things to make your tan last longer, like exfoliating before sunbathing, utilising a tan extender, and moisturising your skin, but it won’t last forever!
How long do tans last?
As mentioned earlier, a tan obtained by sunbaking outside might last 7 to 10 days before the skin’s outer layer exfoliates naturally, but tans can fade in as little as one day if not properly cared for. While there is no scientific evidence to support this, spray tan specialist Jules Von Hep stated in a Marie Claire interview that it’s important to understand the fact for how long does a tan last as people with different skin types may not accept a tan as well in the week before or during their period, so you may want to time your tan accordingly.
Do tans go away naturally?
Yes, a tan will naturally go away due to skin exfoliation. It may not be the most pleasant thought, but the human skin loses and regenerates millions of cells daily. Your body will eventually revert to its natural colour as tanned skin cells are replaced with fresh, untanned ones. Even if you wish your tan would last longer, shedding/generating skin cells exists to protect us.
If you return from a holiday in the sun to a colder environment with little sun, you may notice that your tan will fade even faster. This is because, as the tanned skin cells are shed, the production of melanin (which causes a tan) decreases due to the lack of UV radiation from the sun.
What steps can you take to achieve a great tan?
Preparing your skin before basking in the sun is essential for a healthy, safe, long-lasting tan. Firstly, before you head for the sun loungers, it is necessary to exfoliate your skin. Exfoliating removes dead cells, which could otherwise cause an uneven tan, and ensures that the skin cells you wish to tan are not already at the end of their life cycles.
In addition, you must regularly apply sunscreen to help protect your skin. Sunscreen can’t block 100% of the sun’s UV rays, enabling you to still tan whilst wearing sunscreen. There is no excuse for skipping the sunscreen, as it will help to protect against sunburn, wrinkles, ageing and skin conditions, such as cancer.
Once you are out of the sun, apply an after-sun moisturiser to ensure your skin does not dehydrate and help enable that longer-lasting tan.
Can a tan be permanent?
Tans are always temporary since skin exfoliates naturally over time—the tanned skin flakes off. Older skin sloughs off as new cells develop. Anyone who seems to be “permanently” tanned has darker skin naturally, utilises a sunless tanning lotion or spray tan, or spends a lot of time in the sun.
How to Prevent Tan Fading
You can do a few things to keep your tan from fading and extend its longevity.
- Exfoliate your skin before going out in the sun or obtaining a spray tan. This will protect the skin from flaking and provide a smooth, even surface for a spray tan to adhere to.
- Shower in lukewarm or chilly water. Hot water dehydrates the skin, causing a tan to disappear faster.
- Maintain skin moisture.
- Hydrated skin will delay the exfoliation of your body. Moisturise your skin using a natural oil such as coconut or avocado.
- Use a tan extender or a tanning lotion to help your tan last longer. Some tan extenders enhance melanin synthesis.
Precautions and adverse effects of sun exposure
Always apply sunscreen with an SPF of at least 50 when spending time in the sun. You’ll need to use more sunscreen than you think. After entering the water, reapply sunscreen every 2 to 3 hours.
The hazards of overexposure to sunlight include:
- Sunburn, hot rash, premature ageing (sun causes the skin to lose suppleness, which can cause wrinkles and skin damage)
- Heat-induced dehydration
- Melanoma and other skin cancers
- Eye damage because of looking at the sun
No Comments